Who Pays For Palliative Care?
Palliative treatment is a good option when it comes to alleviation of chronic pain, symptoms and side effects of illnesses. What is not palliative care is essential to understand – it is not hospice treatment. Palliative services are very much different from hospice care because for palliative care you can be cared for while still on treatment.
Payment For Palliative Care

The Medicare, VA benefits and most insurance providers cover palliative care consultations. Co-pays may be required. Although a consultation does not guarantee continued care, it is the first step toward receiving actual care.
If your coverage for Medicare Part A is the same as for other types of medical care, you can be eligible for palliative care. To receive palliative care at home, request a referral to Medicare for home palliative care.
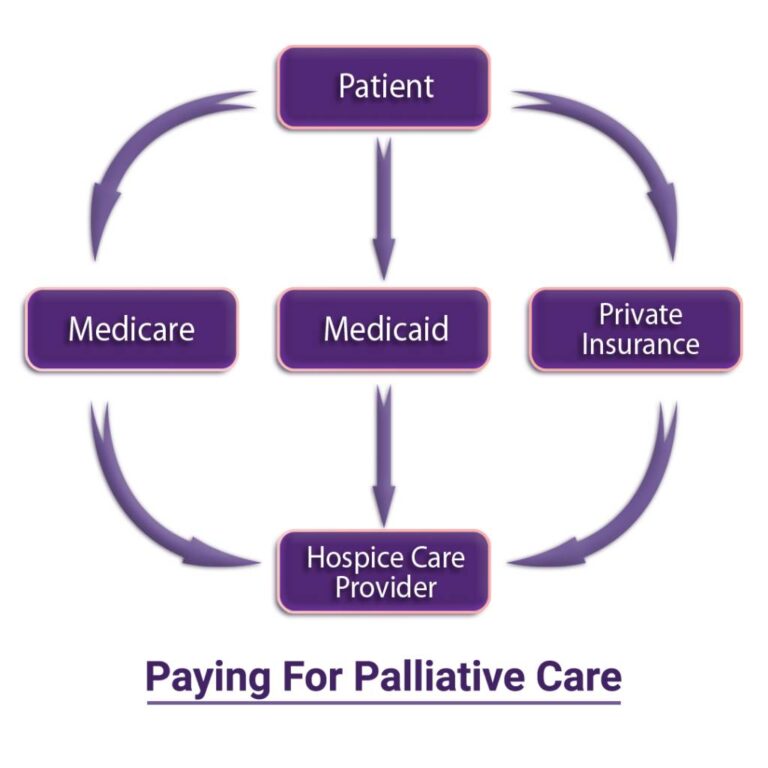
Some of the services and supplies needed to treat your disease may be included if you have Medicare Part B coverage. If you are eligible for Medicaid, specific palliative care treatments and medications may be substituted. Some chronic, long-term or in-hospice private insurance schemes also cover palliative care.
To avoid being surprised by unexpected bills, speak with representatives at the palliative care provider’s office about the services. Following that, contact Medicare, Medicaid or your insurance provider to verify coverage for specific services. Inquire about co-payments for such services as well.
Veterans Affairs facilities have a PCCT team that offers palliative and hospice treatment in VA facilities, community hospitals, community care homes and patient’s home. These services are included in the Medical Benefits Package of the Veterans Administration.
How Does Palliative Care System Work?
Palliative care can be delivered in a hospital, outpatient clinic, nursing home, assisted living facility or at the patient’s home. Palliative care teams use a holistic or full-body approach to help patients improve their quality of life in areas such as:
Management of pain and symptoms This may include prescribing medication or addressing pain and symptoms such as shortness of breath, nausea, dizziness, fatigue and loss of appetite through other means.
Psychological, emotional and spiritual health. “Not all pain is physical,” Each points out. Along with physical symptoms, palliative care can assist in addressing a patient’s mental health. Palliative treatment can include personal counsel, references from psychologists or other providers and meetings with religious or spiritual consultants.
Practical and logistical support is also included, variations of which include coordination of transport, meal delivery and other personalized support, from financial consultation to finding someone to watch your beloved pets at medical appointments.
Are There Any Other Costs?
If a patient receives palliative care but not hospice care, the patient will incur out-of-pocket costs in instances which may include the following:
- Premiums
- Deductibles
- Copayments
- Coinsurance
Regulations and factors to considered:
If a person receives palliative care but is not a hospice patient, Part B of Medicare helps cover the expense. To qualify for Medicare coverage of palliative care in a hospice setting, an individual must meet the following criteria:
- The primary care physician and the hospice physician must certify that the patient is terminally ill and unlikely to live longer than six months.
- An individual must choose palliative care for their comfort over curative or prophylactic treatment.
- A patient must sign a form indicating their preferences for hospice care over treatment-related care.
- Medicare generally covers all hospice-related services, but not living expenses whether patients are in their own home or in assisted living facility.
Who Is Responsible For Paying For Palliative Care?

Palliative care is paid for via multiple sources. Palliative care services are generally covered by standard medical insurance policies. Certain palliative care services may be covered by the following insurance policies:
- Medical Assistance Under Medicare
- Individual health insurance policies or managed care program
1.Medicare
Medicare Part B (medical insurance) may also cover specific palliative care and medicines and visits to doctors, nurses and social workers. Medicare Part B benefits provide coverage of Palliative Care. The palliative care provider will charge Medicare for the services rendered. It is essential to understand the copayments or fees you will have to pay, if any.
2. Assistance with Medical Expenses
Palliative care and medication may be covered if you are enrolled in any Medical Assistance program. Find out what copayments or fees, if any, you will be required to pay and ask for your financial responsibility within the cost and fee schedule before accepting services.
Private Insurance, Health Maintenance Organizations & Managed Care Programs

Managed health care organizations and health maintenance organizations cover several private health insurance plans as part of their hospice or chronic care benefits. Palliative care may be covered under a long-term care policy. Consult your health insurance or long-term care insurance representative for additional information.
